UAS Airspace Restrictions
Navigation restrictions that are applicable to unmanned aircraft systems are published in the UK AIP (Section ENR 5.1 Prohibited, Restricted and Danger Areas) including restrictions applicable around aerodromes (Flight Restriction Zones) and restrictions applicable around other areas. A dataset of all ENR 5.1 UAS Airspace Restrictions is also available as an electronic (digital) file by selecting the UAS Airspace Restrictions File (ENR 5.1) link from the list available on the current IAIP website and which is updated each AIRAC (for additional information regarding digital datasets see below).
For details regarding Flight Restriction Zones around aerodromes see below.
UAS Flight Restriction Zones
The Air Navigation Order, as amended, sets out UAS Flight Restriction Zones (FRZ) around Protected Aerodromes for Unmanned Aircraft operating in the Open and Specific categories.
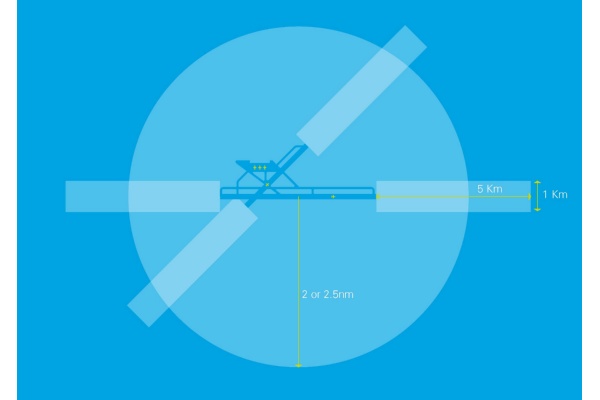
The shape of FRZ is constructed by using the airfield’s existing aerodrome traffic zone and, where applicable, a Runway Protection Zone(s) with a shape five kilometres by one kilometre starting from the point known as the ‘threshold’ at the end of each of the airfield’s runways. Both zones extend upwards to a height of 2,000 feet above the airfield. Certain exceptions apply to the shapes of FRZ and RPZ and information regarding the exact dimensions of each FRZ/RPZ is published in the UK AIP (Section ENR 5.1 Prohibited, Restricted and Danger Areas).
An Aerodromes FRZ and RPZ(s) are contiguous irrespective of how mapping tools may portray them.
It is illegal to fly any drone at any time within these restricted zones unless you have permission from air traffic control at the airport or, if air traffic control is not operational, from the airport itself. (AIP Section ENR 1.1 contains information for UAS operators and aerodromes in relation to requesting and granting permission for any unmanned aircraft flight within an FRZ/RPZ).
A Protected aerodrome is one which is:
> UK Licensed;
> Certified;
> UK Government;
> Prescribed by the secretary of state for the purpose of being Protected.
All Protected aerodromes and details of their FRZ/RPZ Restriction Zones are published in the UK AIP, Section ENR 5.1 Prohibited, Restricted and Danger Areas. Every airfield’s restriction will be different, but the diagram below gives a generic example of what FRZ/RPZ restricted zones look like.
UAS Airspace Restrictions - Digital Datasets
Datasets of all ENR 5.1 airspace restrictions applicable to UAS have been created to allow end users the ability to view the data in separate viewers (Free AIXM Viewers) or integrate with other applications.
The datasets provided as digital files will be delivered in line with the AIRAC Effective Date of the UK AIP AIRAC cycles and will remain effective until replaced.
Developers can download the data files for these areas from the Digital Dataset page.
The dataset is provided in AIXM version 5.1. NATS reserve the right to model aeronautical information (AI) appropriately for AI product production and the right to adopt newer versions of AIXM with prior notification.
Users should check forward/backward compatibility within their applications if using a newer AIXM version in the future to ensure there is no data loss. Please review http://www.aixm.aero/page/aixm-versioning-policy for guidance.
The KMZ file is the KML file Zip-compressed and be opened by a number of programs. Please refer to https://fileinfo.com/extension/kmz
* Visualisation of UAS Airspace volumes has been provided through the use of Keyhole Markup Language (KML), for hours of activation and associated services refer to the AIP and NOTAM Service. Keyhole Markup Language (KML) is an XML language focused on geographic visualisation but does not contain circle geometry, therefore, circle/curved airspace has been created using LineStrings joining points on the circumference of the circle/curve. Due to this limitation when visually zoomed in there can appear to be small gaps between abutting airspace.
This is purely a visualisation constraint for the airspace which is physically contiguous, abutted with a common boundary, for an authoritative definition refer to the AIP.



